Key Points
- AI tools decreased open source software developers’ efficiency by 19 percent
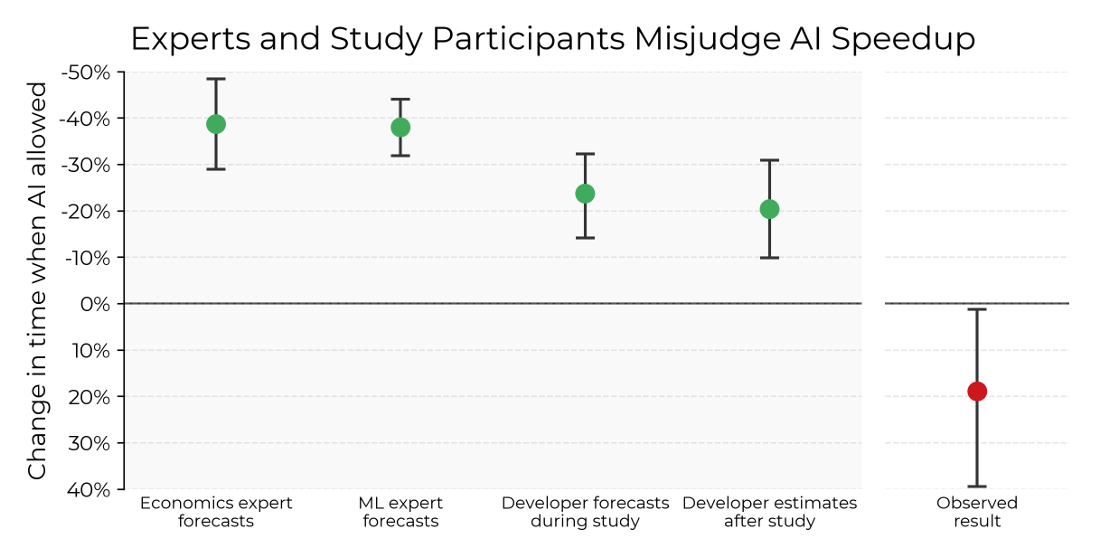
- Developers expected a 24 percent reduction in time needed for tasks with AI tools
- AI-aided tasks took longer to complete than tasks without AI assistance
- Developers spent more time reviewing AI outputs and making changes to generated code
- Less than 44 percent of AI-generated code was accepted without modification

A striking digital artwork featuring an analog clock face on the left side with red hands against a glowing blue background. The clock is surrounded by concentric circular ripples that transition into flowing streams of binary code (1s and 0s) that sweep across the right side of the image. The entire composition is rendered in deep electric blue tones with subtle lighting effects that create a sense of depth and movement.
Introduction to the Study
Researchers at METR conducted a randomized controlled trial to investigate the impact of AI tools on the efficiency of open source software developers. The study involved 16 experienced developers who worked on specific open source repositories, completing 246 individual tasks with and without AI assistance.
The tasks included bug fixes, features, and refactors, and the developers were instructed to use AI tools like Cursor Pro or Anthropic’s Claude for half of the tasks. The time needed to fix pull requests based on reviewer feedback was included in the overall assessment.
Expected Time Savings
Before performing the study, the developers expected the AI tools to lead to a 24 percent reduction in the time needed for their assigned tasks. Even after completing those tasks, the developers believed that the AI tools had made them 20 percent faster, on average.
However, the study found that the AI-aided tasks ended up being completed 19 percent slower than those completed without AI tools. The researchers analyzed screen recording data from a subset of the studied developers and found that AI tools tended to reduce the average time spent actively coding, testing/debugging, or reading/searching for information.
Trade-offs
Despite the initial time savings, the AI tools ultimately led to increased time spent reviewing AI outputs, prompting AI systems, and waiting for AI generations, as well as idle/overhead time. The developers accepted less than 44 percent of the code generated by AI without modification, and a majority reported needing to make changes to the code generated by their AI companion.
A total of 9 percent of the total task time in the AI-assisted portion of the study was taken up by this kind of review. The study’s findings suggest that the use of AI tools may not always lead to increased efficiency for open source software developers.
Source: arstechnica.com
